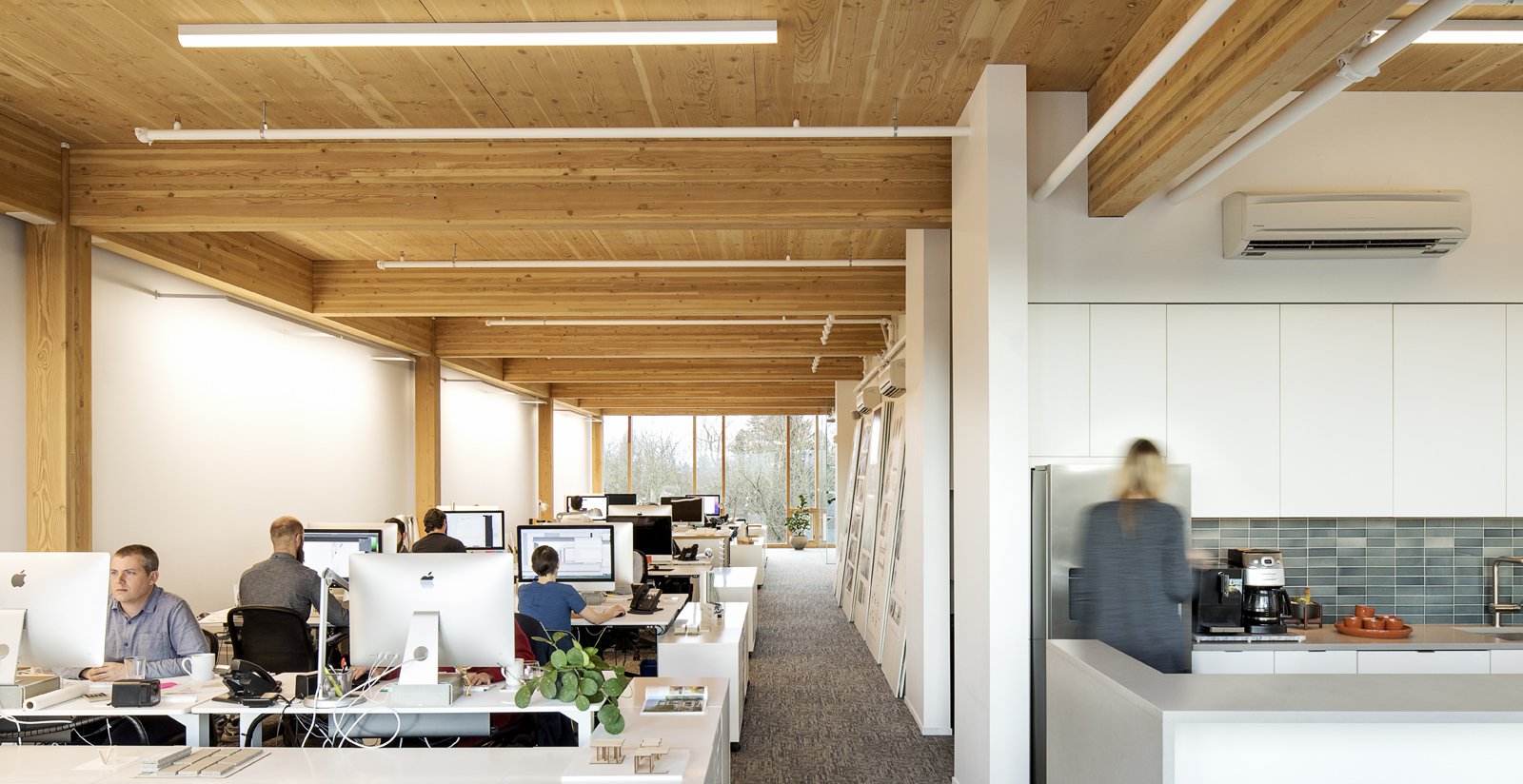
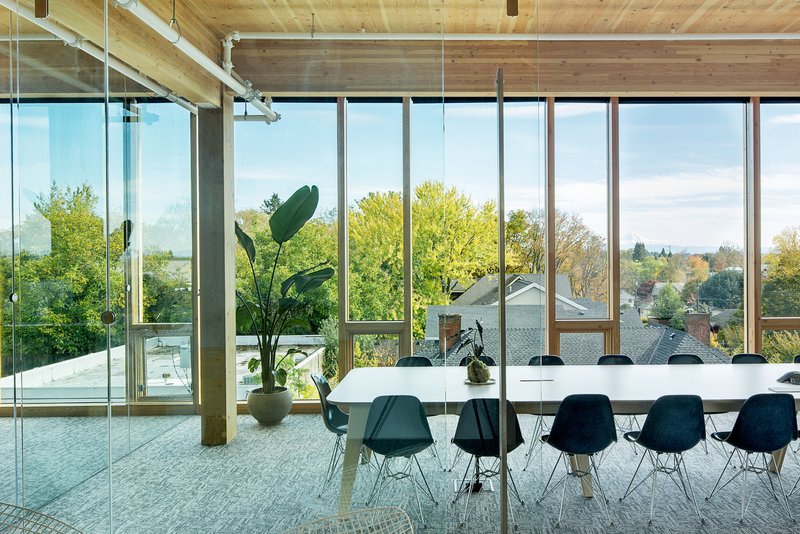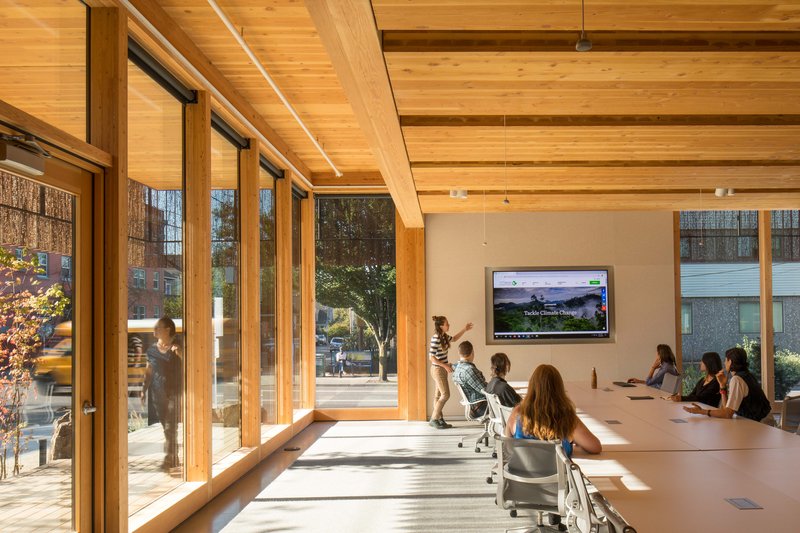
This project evaluated the post-occupancy indoor air quality and occupant comfort at Albina Yard. A research team from the University of Oregon monitored Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) for over a year following the building's construction to better understand the impact that exposed wood structures have on indoor air quality and occupant comfort.
IEQ of buildings include aspects of the built environment that affect occupant health and well-being such as indoor air quality, thermal comfort, visual comfort, and acoustic comfort. The contribution of wood in creating healthy environments has been discussed in several research studies, many of which are based on occupant feedback rather than on quantitative monitoring data. Most quantitative IEQ studies are limited to measurements in a laboratory environment or in unoccupied buildings, or only monitor data related to one single IEQ performance indicator. This is one of the first studies of an occupied mass timber building that analyzed data in three areas that impact occupant experience: indoor air quality, bacterial community composition, and floor vibration. Overall, the building was found to perform well in these areas.
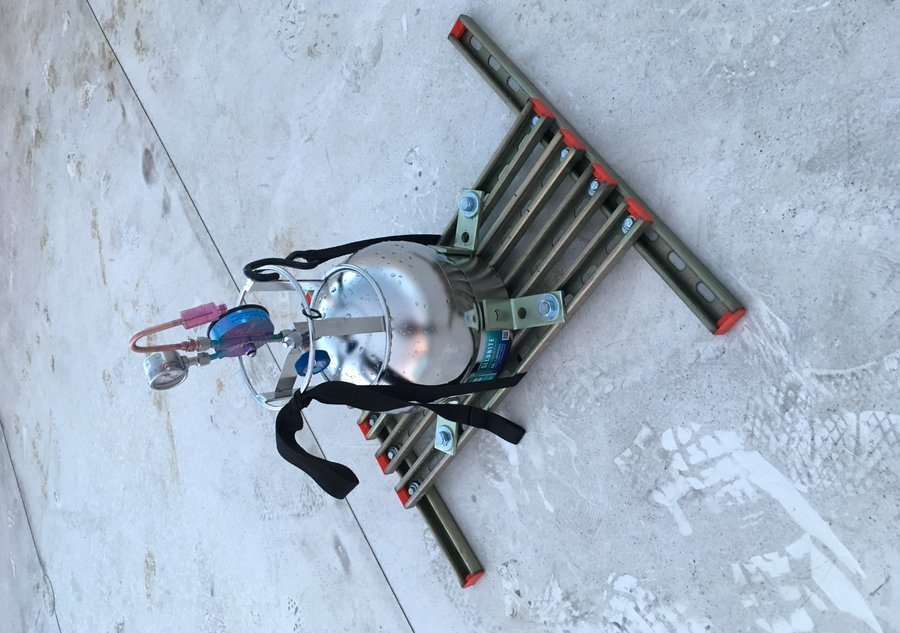

Whole air sampler located on the roof
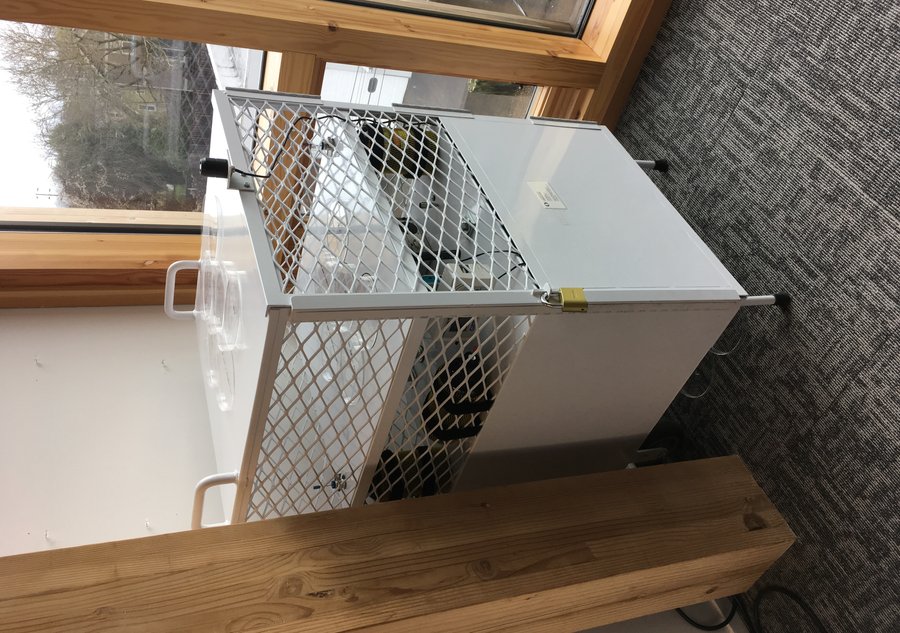

Air quality monitoring kit and passive microbial sampler
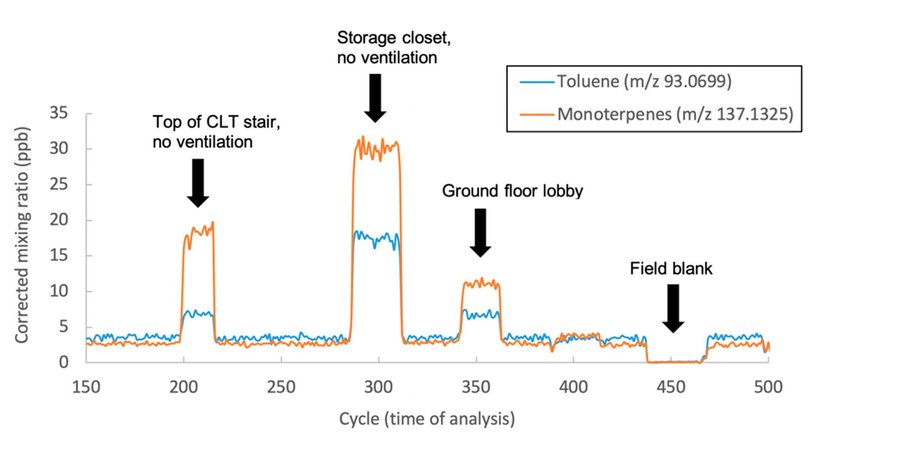
Six common VOCs were selected for analysis: acetone, formaldehyde, methanol, benzene, toluene and monoterpenes. Above are results for toluene and monoterpenes one-minute grab samples from various building locations and one field blank canister.
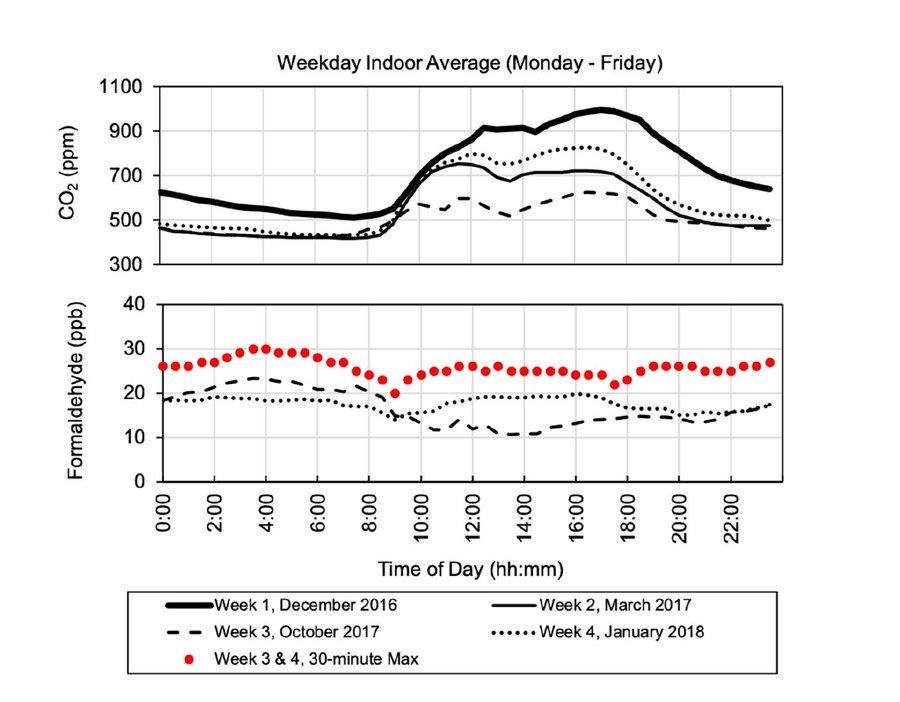
Average indoor Carbon Dioxide and Formaldehyde levels at various times of day monitored in the fourth floor open office area.




